16 real(dp),
dimension(:, :),
allocatable :: data
45 real(dp),
dimension(:),
pointer :: phi
46 type(
array2d),
allocatable,
dimension(:) :: r
66 integer(I4B) :: n, nodes
73 allocate (gradient%R(dis%nodes))
75 gradient%R(n)%data = gradient%create_gradient_reconstruction_matrix(n)
82 integer(I4B),
intent(in) :: n
83 real(dp),
dimension(:, :),
allocatable :: r
85 integer(I4B) :: number_connections
86 integer(I4B) :: ipos, local_pos, m
88 real(dp),
dimension(3) :: dnm
89 real(dp),
dimension(:, :),
allocatable :: d
90 real(dp),
dimension(:, :),
allocatable :: inverse_distance
95 allocate (d(number_connections, 3))
96 allocate (r(3, number_connections))
97 allocate (inverse_distance(number_connections, number_connections))
105 do ipos = this%dis%con%ia(n) + 1, this%dis%con%ia(n + 1) - 1
106 m = this%dis%con%ja(ipos)
111 d(local_pos, :) = dnm / length
112 inverse_distance(local_pos, local_pos) = 1.0_dp / length
114 local_pos = local_pos + 1
118 r = matmul(
pinv(d), inverse_distance)
122 function get(this, n)
result(grad_c)
125 integer(I4B),
intent(in) :: n
127 real(dp),
dimension(3) :: grad_c
129 grad_c = this%compute_cell_gradient(n)
135 real(DP),
dimension(:),
pointer,
intent(in) :: phi
142 real(dp),
dimension(3) :: grad_c
145 integer(I4B),
intent(in) :: n
147 real(dp),
dimension(:, :),
pointer :: r
148 integer(I4B) :: ipos, local_pos
149 integer(I4B) :: number_connections
152 real(dp),
dimension(:),
allocatable :: dc
156 allocate (dc(number_connections))
158 do ipos = this%dis%con%ia(n) + 1, this%dis%con%ia(n + 1) - 1
159 m = this%dis%con%ja(ipos)
160 dc(local_pos) = this%phi(m) - this%phi(n)
161 local_pos = local_pos + 1
166 grad_c = matmul(r, dc)
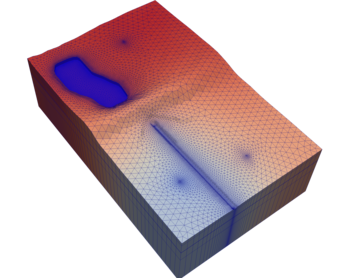
This module contains simulation constants.
real(dp), parameter done
real constant 1
integer(i4b) function, public number_connected_faces(dis, n)
Returns the number of connected faces for a given cell.
real(dp) function, dimension(3), public node_distance(dis, n, m)
Returns the vector distance from cell n to cell m.
This module defines variable data types.
real(dp) function, dimension(3) get(this, n)
real(dp) function, dimension(:, :), allocatable create_gradient_reconstruction_matrix(this, n)
subroutine set_field(this, phi)
real(dp) function, dimension(3) compute_cell_gradient(this, n)
type(leastsquaresgradienttype) function constructor(dis)
real(dp) function, dimension(size(a, dim=2), size(a, dim=1)), public pinv(A)
Abstract interface for cell-based gradient computation.
Weighted least-squares gradient method for structured and unstructured grids.